ERASMUS+ is the EU’s go-to programme for education and training. The programme offers international opportunities to study, work, teach, train, and exchange ideas and good practice. It is also the programme for innovation and developing new solutions and excellence in education and training together with colleagues from across Europe and beyond. It is a very extensive programme with plenty of opportunities for both individuals and organisations covering the whole spectrum from pre-school and primary school, over vocational education to higher education as well as adult education. In this short article we will give you a brief appetizer.

The programme is open to schools, educational and knowledge institutions, municipalities, cultural institutions, regions, as well as other public or private organizations, companies, industry associations, trade organisations etc. And both students, trainees, apprentices, pupils, young people, volunteers, researchers, teachers, course leaders and other staff, can participate in the activities.
ERASMUS+ ACTIVITIES
The activities of the programme are structured around four key activities:
I. LEARNING MOBILITY (Key action 1) This part of the programme provides funding for organisations to offer pupils, students, teachers and trainers, learners and staff the opportunity to go abroad for studying, teaching and training including for example job shadowing.
The Learning mobility programme runs every year and roughly follows the annual cycle illustrated below:

II. COOPERATION PROJECTS (Key action 2) This part of the programme provides funding to support educational institutions and other organisations across the fields of education and training, as well as businesses, trade organisations and public bodies and authorities in order to develop partnerships to share best practice and to work collaboratively to improve the quality, inclusion and equity, excellence, creativity and innovation in education and training.
Five levels of European cooperation projects
With the new Erasmus + 2021-2027 programme we now have a programme that makes it possible to work with knowledge sharing, development and innovation at five levels, covering the full spectrum from small-scale trail projects to large strategic development initiatives:
Small-scale Partnerships: These small partnerships of 6-24 months duration with reduced requirements for administration are designed to make it easier to get started with Erasmus + projects as well as making it possible to test new ideas on a smaller scale and develop your international networks, etc.
Cooperation Partnerships: Formerly known as Strategic Partnerships, this is the core part of the programme we apply to the development of new teaching and training initiatives, didactic methods, ways of collaborating, the sharing of knowledge, exchanging of good practice, etc.
Partnerships for Innovation – Alliances for Innovation: Innovation partnerships, Alliances for Innovation aimes at strengthening Europe’s innovation capacity by boosting innovation through collaboration and the flow of knowledge between higher education, vocational education and the wider socio-economic context, including research.
Forward-looking projects: Large-scale projects that aim to identify, develop, test and / or assess innovative (political) approaches that have the potential to form schools and thereby improve education and training systems.
Partnerships for Excellence: With this initiative, the programme addresses the development of the European education of the future – both to make education more competitive and to strengthen European innovation and competitiveness. This new category of projects consists of Centres of Vocational Excellence, Erasmus+ Teacher Academies and Erasmus Mundus initiatives.
Examples of concrete KA2 project results:
- Curricula and teaching courses
- New forms of learning (eg distance learning, part-time studies and modular courses)
- Materials and methods for teaching
- Project-based collaboration, workshops, virtual laboratories and collaboration forums
- Capacity building and networking activities
- Strategic collaboration plans
- Information, guidance and counselling activities
- Studies, comparative analyses, collection of empirical data and case studies
- Concepts for working with competence-based profiles
- Concepts for credit transfer, quality assurance and recognition of competencies
PRIORITIES: As part of the European collaboration on education and training, the Commission sets the common priorities and objectives on a yearly basis to be pursued by the ERASMUS+ programme. This means that any cooperation project should be designed to contribute to the achievement of these priorities, through their work and results. The priorities consist of two kinds of priorities: General priorities applying to all Erasmus+ sectors and sector specific priorities defined specifically for each educational sector. For more information on the priorities and how they apply to your project, please take a look in the annual programme guide.
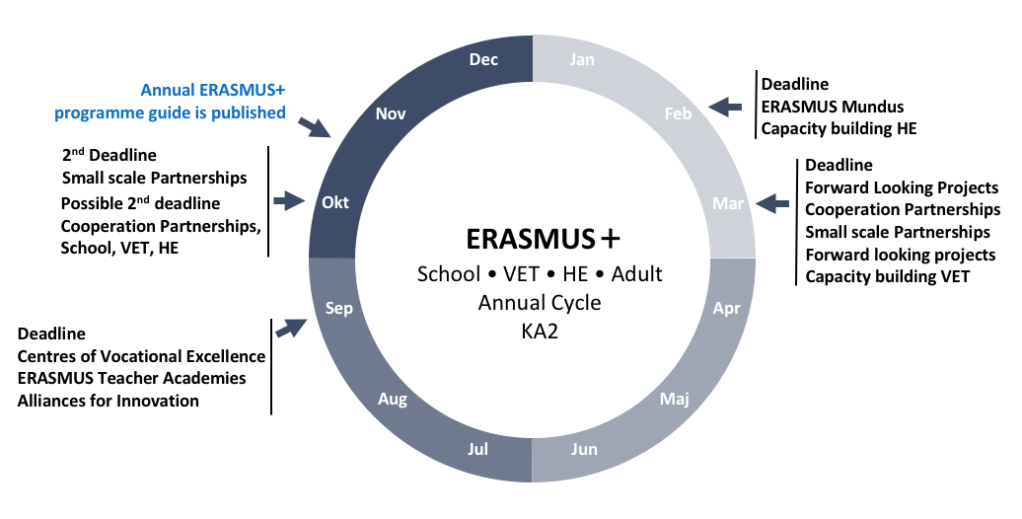
The programme for Cooperation projects also runs every year and roughly follows the annual cycle illustrated below:
On top of the two main activities, the programme also supports policy development and the spreading of knowledge about the European Union in the key action 3 and Jean Monnet actions respectively.
III. POLICY DEVELOPMENT (Key Action 3) The programme also provides support for organisations to cooperate in projects that contribute to the development of new policies, which can trigger modernisation and reforms, at the European Union and system level, within education and training.
IV. JEAN MONNET ACTIONS The Jean Monnet Actions is designed to contribute to the spreading of knowledge about the European Union and European integration within higher education and in other fields of education and training.
Within higher education, this includes for example teaching and research in the field of European Union studies. Within other fields of education, the focus is on teaching about the objectives and the functioning of the European Union in order to encourage active citizenship and to promote the values of freedom, tolerance and non-discrimination. This is done, for example, through education activities for teachers in schools, in youth education and in Vocational Education and Training.
